
Autoimmune Conditions and Flare-Ups in Skin & Scalp Health
-
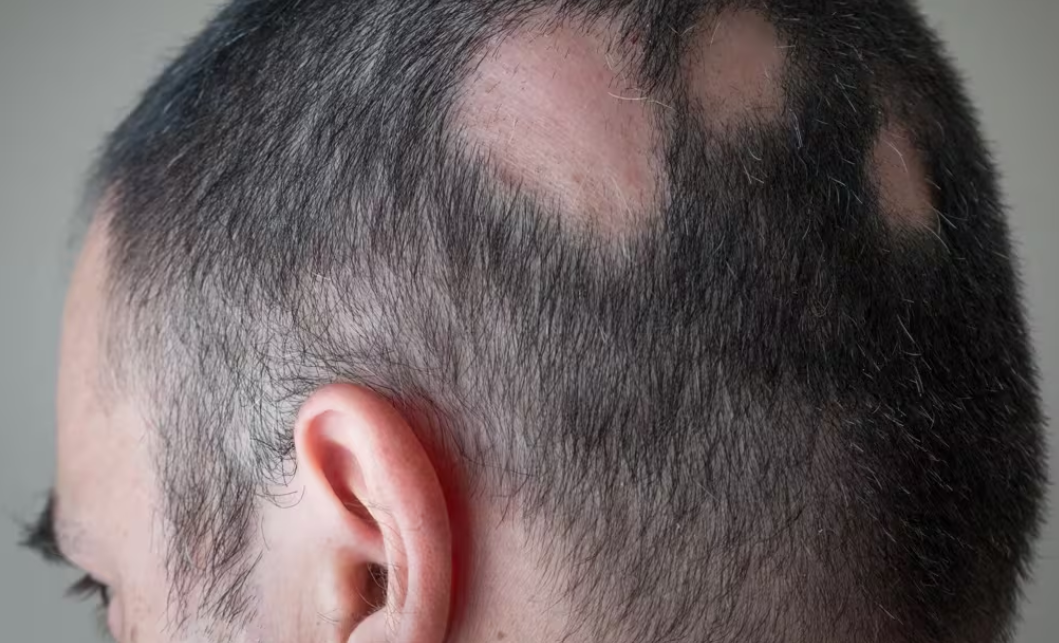
Alopecia
Hair loss caused by immune attack on hair follicles.
-
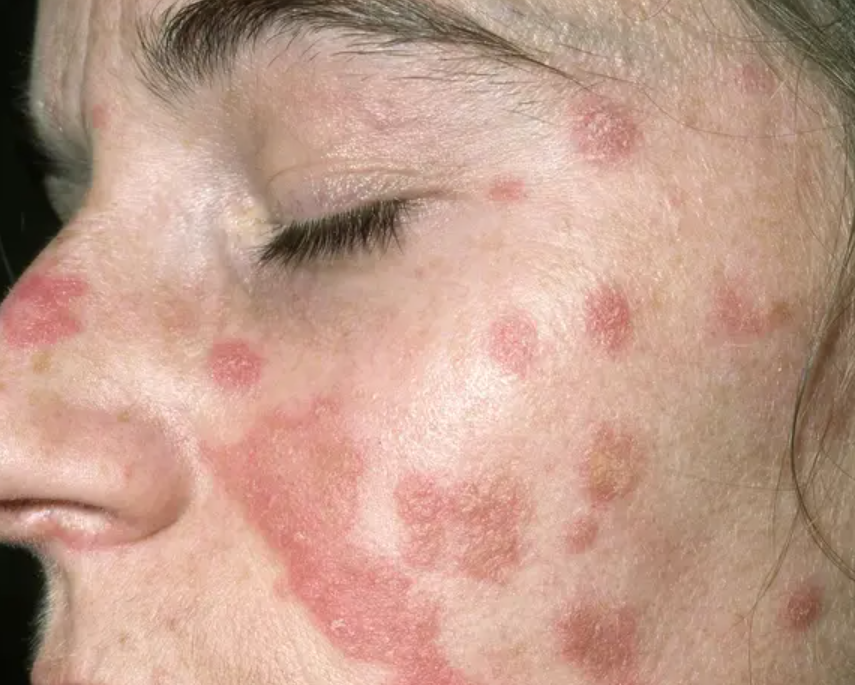
Psoriasis
Accelerated skin cell turnover causing red, scaly plaques.
-
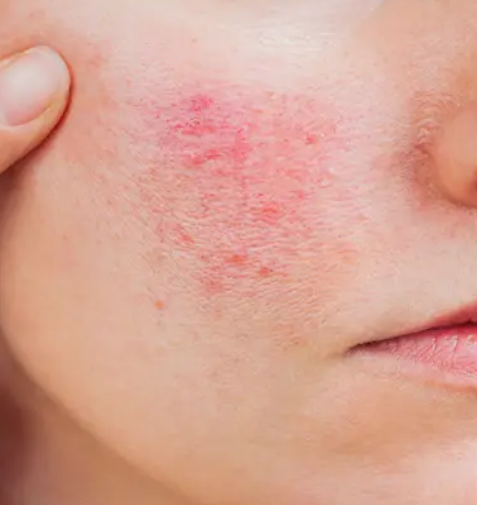
Eczema
Inflammatory skin condition that causes itching, dryness, and flaky patches. Can overlap with autoimmune triggers, increasing barrier sensitivity.
-
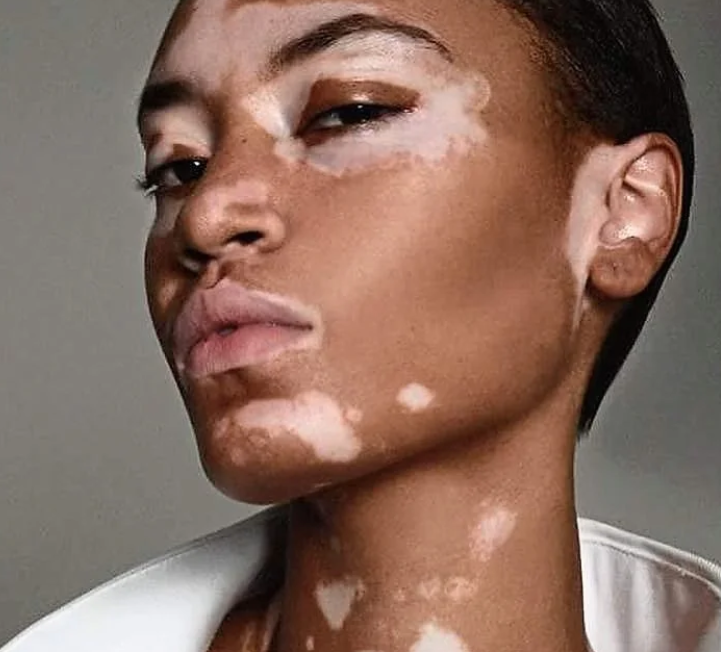

Vitiligo
Loss of pigment in patches due to immune attack on melanocytes.
-
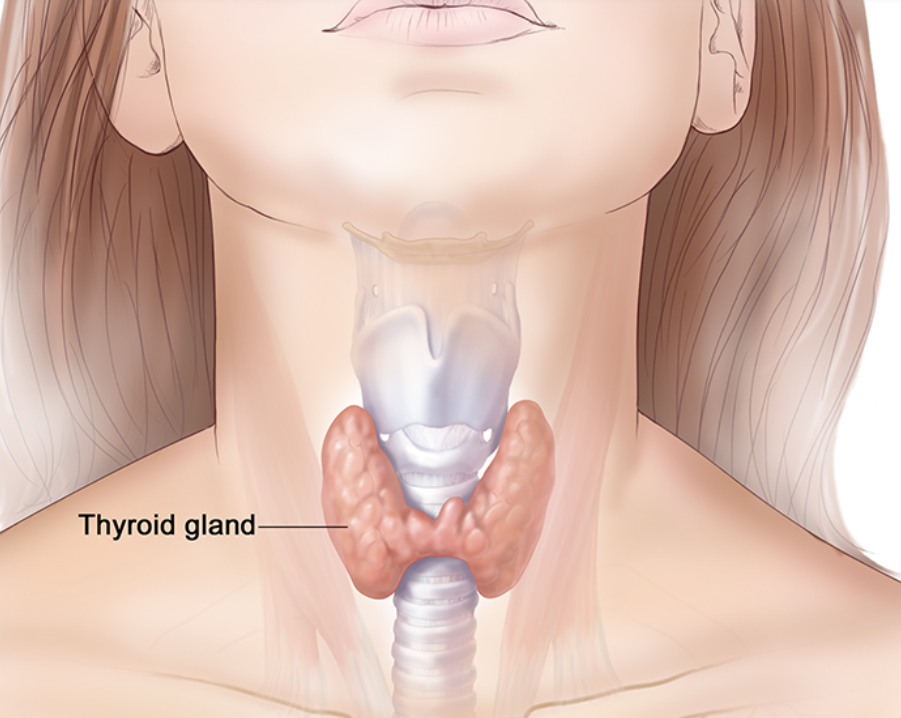
Graves / Hashimotos Disease
Autoimmune thyroid diseases. Can affect skin and hair through hormonal imbalance.
-
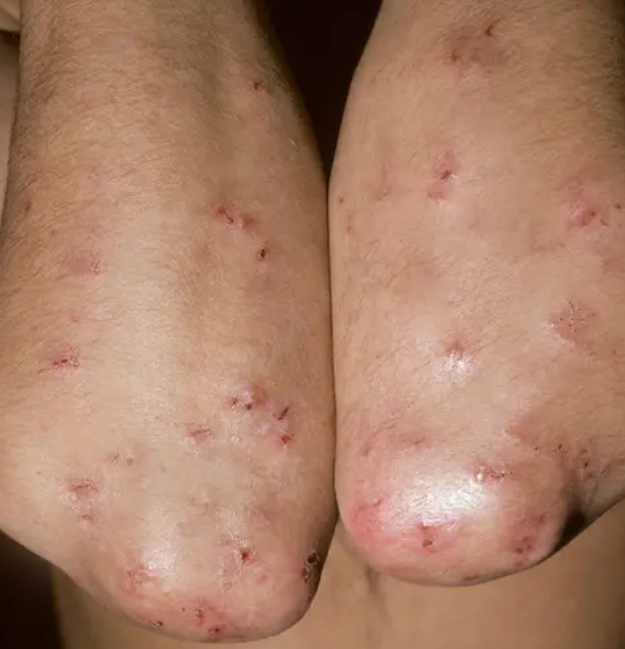
Celiac Disease
Immune reaction to gluten, may cause dermatitis herpetiformis, itchy bumps on elbows, knees, or scalp.

Typical Signs of Flare-Ups
Sudden redness or inflammation
Itching, burning, or irritation
Increased scaling, flaking, or dryness
Hair shedding or thinning on the scalp
Painful or sensitive skin in affected areas
Key Triggers for Flare-Ups
Stress and hormonal changes: Can activate immune responses.
Environmental factors: Extreme heat, cold, or sun exposure.
Skincare products: Strong acids, retinoids, fragrances, or alcohol-based products.
Diet or medication changes: Certain foods or medications may exacerbate inflammation.
Physical trauma: Over-exfoliation, aggressive brushing, or scalp treatments.
Skincare Strategies During Flare-Ups
Simplify your routine: Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturisers.
Barrier repair: Ingredients like ceramides, squalane, panthenol, and colloidal oatmeal help strengthen the skin.
Soothing and anti-inflammatory actives: Centella asiatica, aloe vera, bisabolol.
Avoid triggers: Stop exfoliants, retinoids, strong acids, or other irritants until flare resolves.
Hydration is key: Humectants like hyaluronic acid or glycerin support skin hydration.
Scalp Care During Flare-Ups
Use gentle, non-stripping shampoos
Avoid sulfates, fragrances, and harsh surfactants
Limit heat styling and tight hairstyles
Consider medicated or barrier-supportive scalp treatments under professional guidance
Treat hair loss or shedding gently: avoid vigorous brushing or chemical treatments
In-Clinic Support
LED therapy: Reduces inflammation and promotes healing.
Barrier-repair facials and scalp treatments: Hydrate, calm, and protect sensitive areas.
Microneedling or light resurfacing: Only when skin/scalp is stable.
Targeted treatments for hair loss: Immune-mediated hair loss may benefit from polynucleotides, PRP, or other clinically appropriate interventions.
When to Seek Professional Advice
Flare-ups are frequent, severe, or worsening
Signs of infection (oozing, crusting, redness spreading)
Rapid hair loss or scalp inflammation
Pain, irritation, or compromised barrier persists despite gentle care
Professional assessment ensures a safe, tailored approach to both skincare and scalp health while minimising the risk of aggravating an autoimmune flare.

