
A Guide To Common Skin Concerns
-
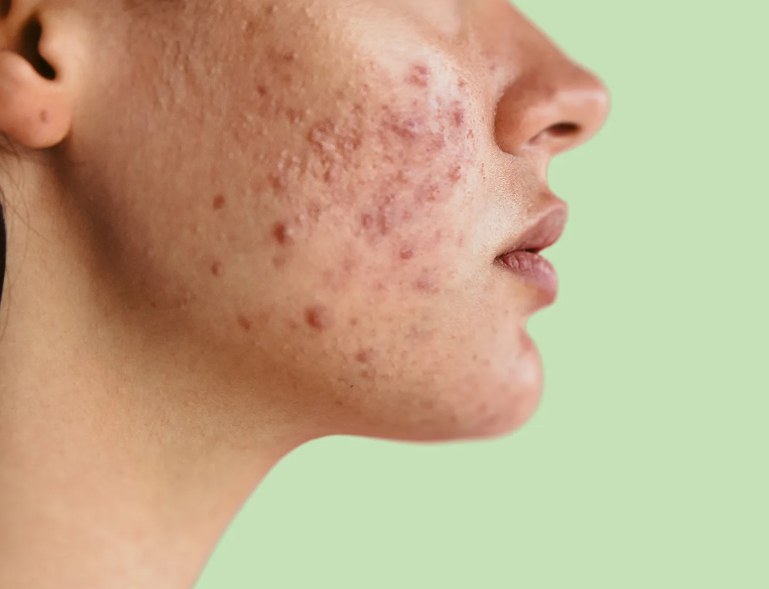
Acne & Breakouts
What it is:
A chronic inflammatory condition involving excess oil, clogged pores, bacteria, and inflammation.Common signs:
Blackheads, whiteheads, pustules
Deep, painful cysts
Texture and congestion
Post-breakout marks
Key triggers:
Hormonal shifts, stress, incorrect skincare, occlusive makeup, diet patterns, medications, and genetics.What helps:
Salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, retinoids
Barrier repair (ceramides, niacinamide)
Consistent exfoliation
In-clinic: microneedling, chemical peels, LED, targeted facials
-
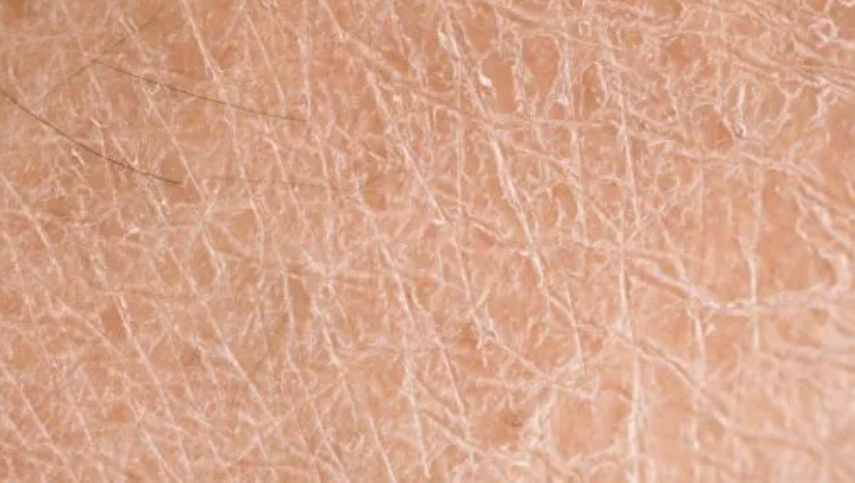
Dehydration
What it is:
A lack of water in the skin (not the same as dry skin, which lacks oil).Common signs:
Tightness
Dullness
Fine lines that look “creased”
Creasing under makeup
Key triggers:
Barrier disruption, harsh cleansers, cold weather, over-exfoliating, caffeine/alcohol.What helps:
Humectants (hyaluronic acid, glycerin)
Occlusives to prevent water loss
Skin-barrier repairing routines
Hydrating facials, gentle peels, skin boosters
-
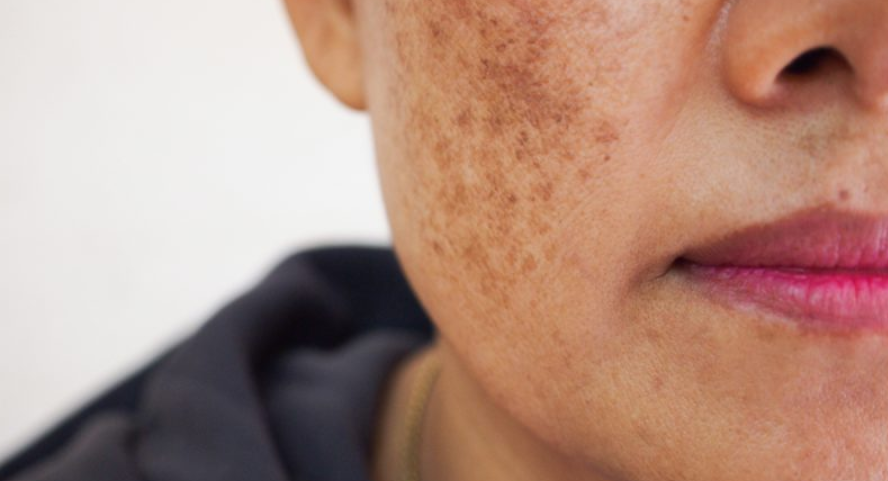
Hyperpigmentation
What it is:
Excess pigment in the skin due to inflammation, UV exposure, or hormonal triggers.Common signs:
Dark spots
Uneven skin tone
Melasma patches
Post-inflammatory marks after acne
Key triggers:
Sun exposure, heat, hormones (pregnancy, contraception), inflammation.What helps:
Vitamin C, azelaic acid, niacinamide
Retinoids for long-term improvement
Consistent SPF
In-clinic: chemical peels, microneedling, advanced brightening treatments
-
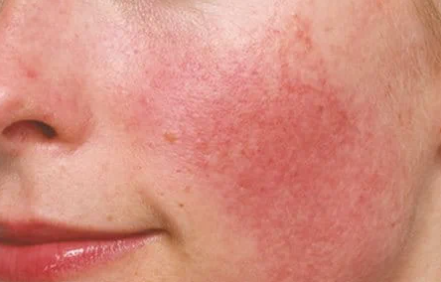
Redness & Sensitivity
What it is:
Heightened reactivity of the skin or underlying inflammatory disorders.Common signs:
Flushing
Burning/stinging after products
Visible capillaries
Easily irritated skin
Key triggers:
Barrier damage, over-exfoliation, weather changes, harsh products, rosacea, genetics.What helps:
Barrier repair ingredients (ceramides, fatty acids, panthenol)
Anti-inflammatory ingredients (centella, green tea)
Fragrance-free routines
In-clinic: LED therapy, soothing facials, gentle exfoliation if appropriate
-
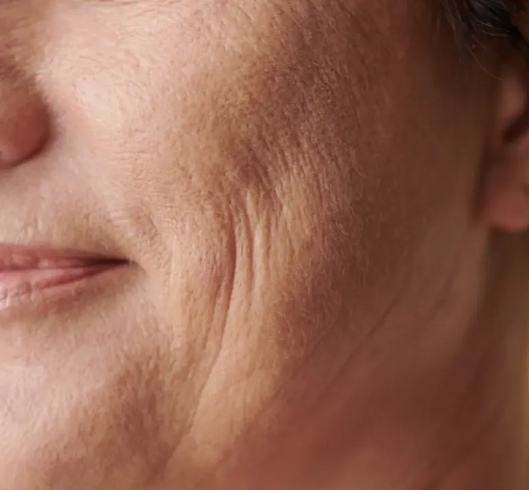

Fine Lines & Wrinkles
What it is:
A natural decline in collagen, elastin, and hydration as we age.Common signs:
Fine lines
Loss of firmness
Texture changes
Dullness
Key triggers:
UV exposure, lifestyle habits, stress, genetics.What helps:
Retinoids, peptides, antioxidants
Daily SPF
In-clinic: microneedling, peels, skin boosters, collagen-stimulating treatments
-
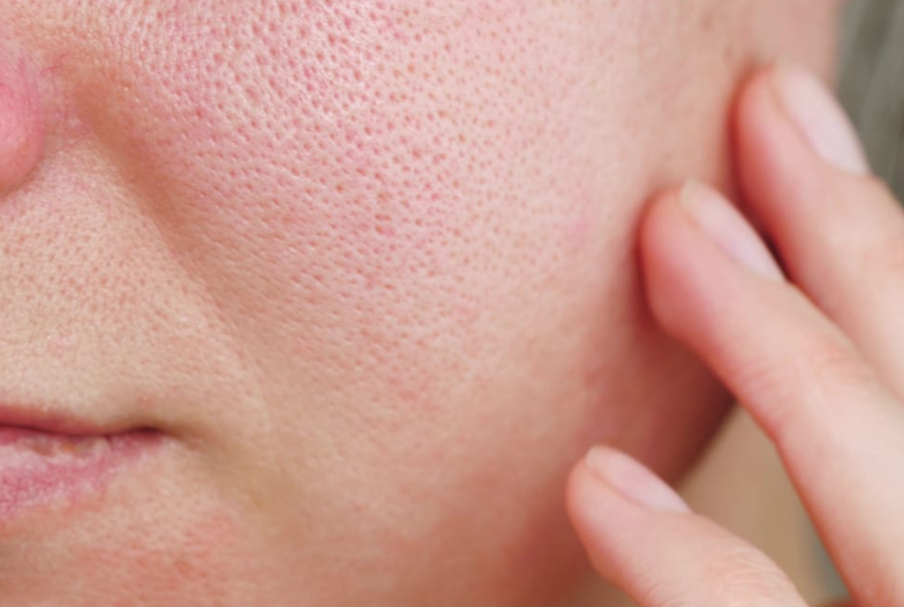
Enlarged / Congested Pores
What it is:
Pores can appear larger when filled with oil/debris, or due to collagen decline.Common signs:
Visible pores
Blackheads
Rough texture
Key triggers:
Excess oil, dead skin buildup, genetics, ageing.What helps:
Salicylic acid
Retinoids
Clay masks
Extractions, deep cleansing facials, microneedling
-
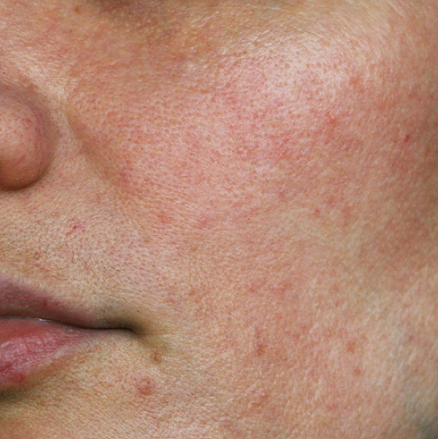
Uneven Texture
What it is:
Irregularities on the surface of the skin.Common signs:
Bumps
Roughness
Patchiness
Old acne marks
Key triggers:
Congestion, dryness, sun damage, slow cell turnover.What helps:
Chemical exfoliants (AHAs/BHAs)
Retinoids
Microneedling, targeted peels
Consistent barrier-focused skincare
-
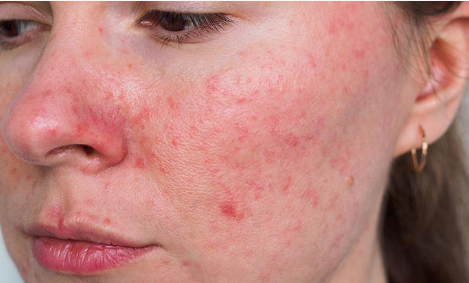
Rosacea
What it is:
A chronic inflammatory skin condition.Common signs:
Persistent redness
Flushing
Sensitivity
Visible vessels
Papules (acne-like bumps)
Key triggers:
Heat, alcohol, spicy foods, stress, UV exposure.What helps:
Anti-inflammatory routines
Avoiding triggers
Azelaic acid
In-clinic: LED, gentle peels, barrier repair treatments
-
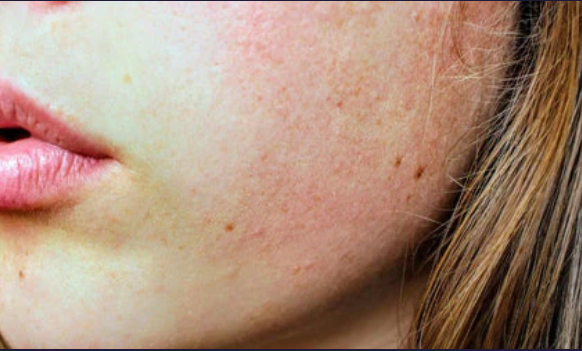
Barrier Damage
What it is:
A compromised skin barrier that can no longer retain moisture or protect against irritants.Common signs:
Burning/stinging
Redness
Flaking
Sudden sensitivities
Breakouts despite “good” routines
Key triggers:
Over-exfoliating, strong actives, stress, weather, illness, retinoid misuse.What helps:
Ceramides, squalane, hydration, omega 3
Removing unnecessary products
Gentle cleansing
Barrier-focused facials
-
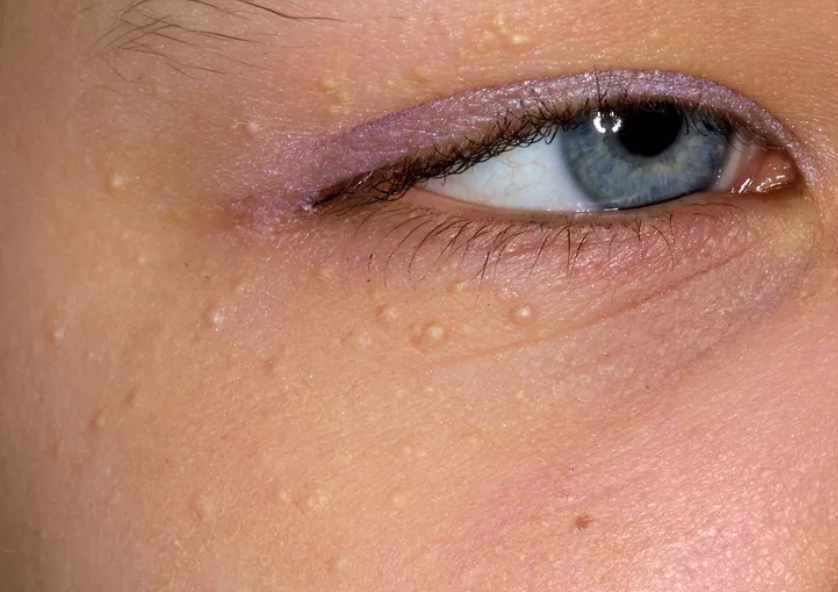

Milia
What it is:
Small, white cysts caused by trapped keratin.Common signs:
Hard white bumps
Common around eyes and cheeks
Key triggers:
Heavy creams, lack of exfoliation, genetics.What helps:
Gentle exfoliation (AHAs)
Retinoids
Professional extractions
-
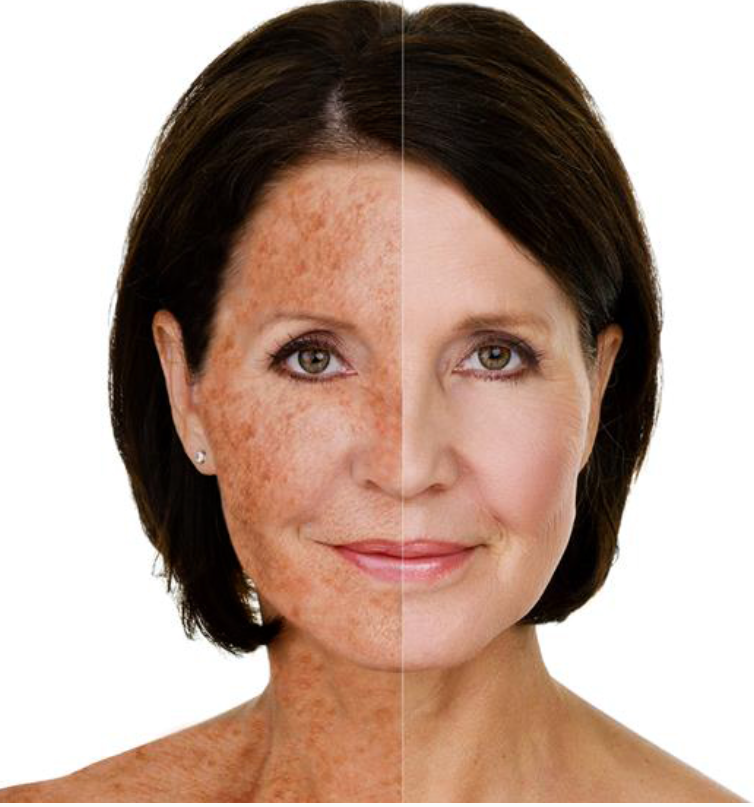

Sun Damage
What it is:
Long-term UV damage to the skin.Common signs:
Pigment patches
Roughness
Fine lines
Loss of elasticity
What helps:
Daily SPF
Antioxidants
Retinoids
Chemical peels, microneedling, targeted resurfacing
-
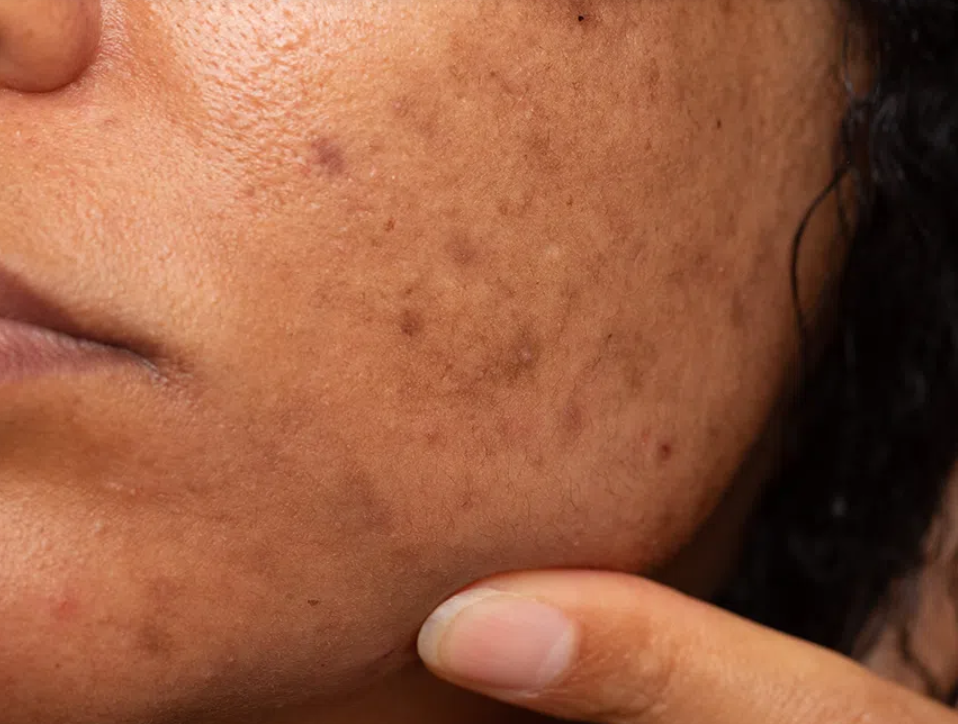
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
What it is:
Dark marks after inflammation, common in medium-to-deep skin tones.Common signs:
Brown marks after acne or irritation
What helps:
Brightening actives
SPF
Microneedling & peels (with careful skin-type assessment)
-
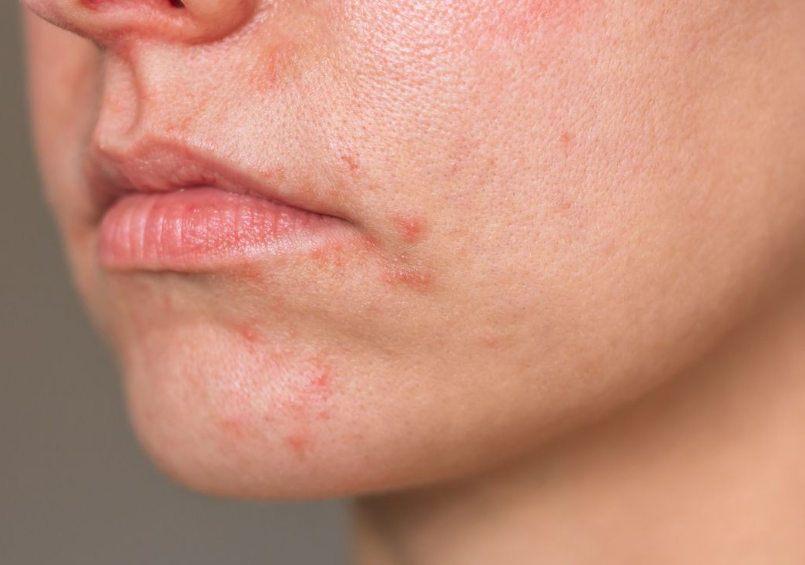
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
What it is:
A chronic inflammatory skin condition caused by a weakened skin barrier and an overactive immune response. It leads to dryness, irritation, and recurring flare-ups.Common signs:
Rough, dry, or scaly patches
Redness or inflammation
Itching (often severe)
Cracking or flaking
Occasional oozing or crusting during active flare-ups
Thickened skin from long-term scratching
Key triggers:
Fragranced products, hot showers, harsh cleansers, stress, allergens, cold weather, friction, wool fabrics, over-exfoliating, household detergents.What helps:
Gentle, fragrance-free skincare
Rich moisturisers focusing on barrier repair
Ceramides, cholesterol, fatty acids, squalane, oat extract, panthenol
Humectants like glycerin or low % urea
Anti-inflammatory ingredients: colloidal oatmeal, centella, aloe, bisabolol
Avoiding unnecessary actives during flares
In-clinic options that may support eczema-prone skin:
LED light therapy (anti-inflammatory)
Hydrating, soothing facials suitable for sensitive skin
Gentle peels only when skin is stable
Barrier-focused treatments (case-by-case)
When to seek medical advice:
If eczema becomes frequent or severe, shows signs of infection, affects sleep, appears on the eyelids, or doesn’t improve with barrier care. -
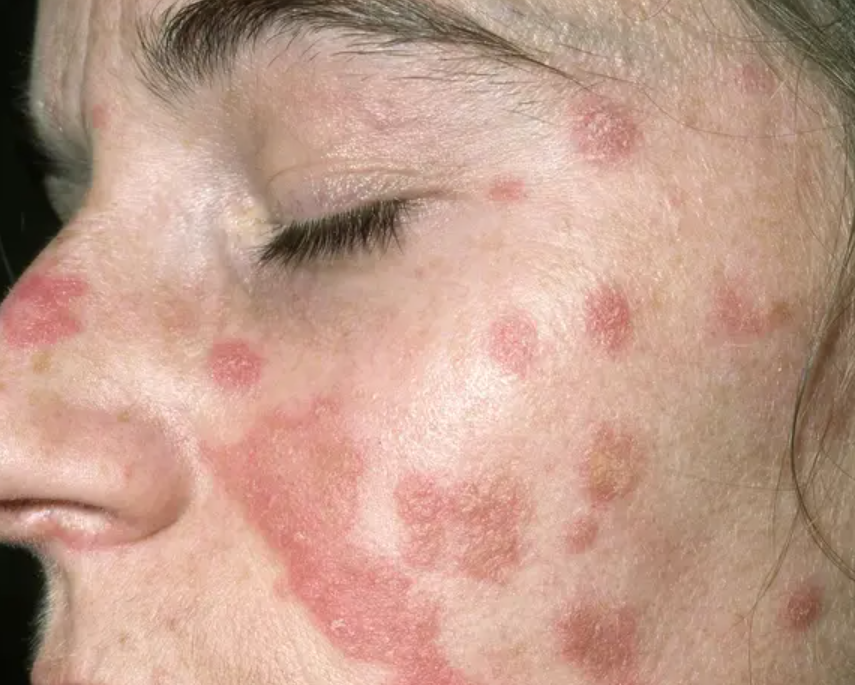
Psoriasis
What it is:
A chronic autoimmune skin condition where skin cells multiply too quickly, leading to thick, scaly, inflamed patches. It often runs in families and can flare with stress, illness, or certain medications.Common signs:
Thick, silvery or white scales
Red, inflamed plaques
Flaking or shedding
Itching or burning
Patches commonly on elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back
Nail pitting or thickening in some cases
Key triggers:
Stress, cold weather, illness, skin injury, certain medications, alcohol, smoking, friction, and infections such as strep throat.What helps:
Gentle, fragrance-free skincare
Regular moisturising to reduce scaling and dryness
Ingredients that calm inflammation: niacinamide, panthenol, oat extract
Avoiding strong acids or retinoids on affected areas
Scalp-friendly soothing routines if patches occur on the scalp
In-clinic options that may support psoriasis-prone skin:
(When the skin is stable and not cracked or bleeding)LED light therapy (supports inflammation control)
Hydrating, non-irritating facials
Scalp treatments designed to soothe rather than exfoliate aggressively
When to seek medical advice:
If plaques are painful, widespread, rapidly worsening, infected, affecting nails, or impacting quality of life. Prescription treatments such as topical steroids. -
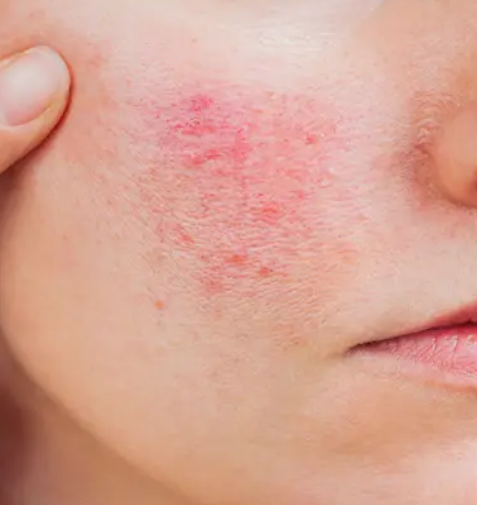
Perioral Dermatitis
What it is:
A stubborn inflammatory rash that appears around the mouth, nose, and sometimes the eyes. It’s commonly triggered by topical steroids, harsh products, or barrier disruption.Common signs:
Small red bumps
Burning or stinging
Flaky or dry skin around the mouth
Rash that worsens with heavy moisturisers or steroid creams
Clear zone directly next to the lips, with redness around it
Key triggers:
Topical steroid creams, strong actives (retinoids/AHAs/BHAs), toothpaste with SLS, heavy or occlusive moisturisers, over-cleansing, fragranced products, hormonal fluctuations.What helps:
Stripping routines right back to gentle basics
Fragrance-free, minimal skincare
Barrier repair ingredients: ceramides, squalane, panthenol
Avoiding exfoliants, retinoids, and occlusive balms until fully settled
Switching to SLS-free toothpaste
In-clinic options that may support recovery:
(Only when active inflammation has calmed and barrier is stable)LED light therapy
Soothing facials focused on hydration and calming
No peels or strong actives until fully resolved
When to seek medical advice:
If the rash persists, worsens, spreads around the eyes, or was triggered by topical steroids. Medical treatment often includes prescription topical or oral antibiotics, which are very effective.

